The Difference between Downstream and Upstream
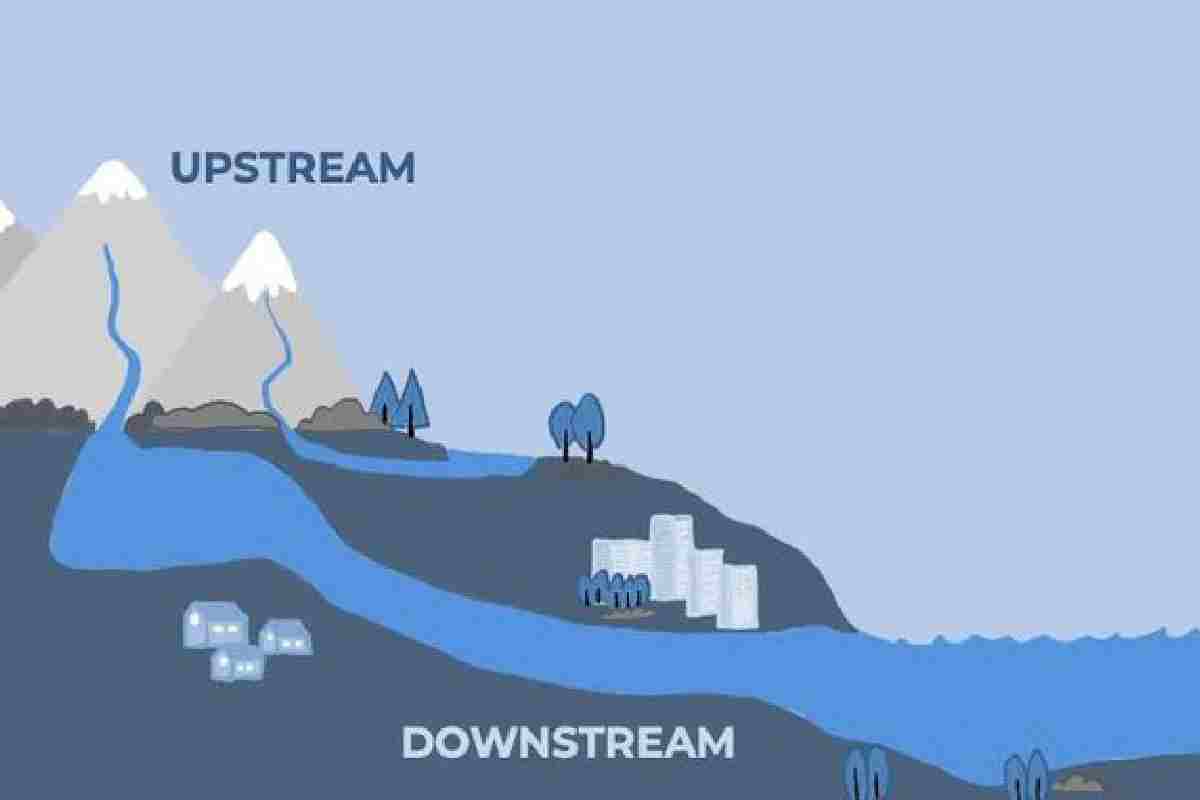
Table of Contents
What does Downstream mean?
In IT, “downstream” denotes the data program to an end-user or end-user from a central server or point of origin. It is in contrast to upstream transfers that travel from the end-user to the central repository. The standings “uploads” and “downloads” refer to upstream and downstream transmissions, respectively.
Upstream and Downstream Processing
The production of active ingredients (API) of biopharmaceuticals generally begins with producing the active ingredient through living cells, the so-called upstream process, followed by the purification of the target active ingredient or the downstream process.
Upstream Processing
The first steps in the upstream process begin with milliliters of mammalian or microbial cells engineered to produce a specific protein molecule. Through numerous stages of culture in a controlled environment within a bioreactor, these cell cultures are grown to a volume of several thousand liters to produce several kilograms of the desired active ingredient.
Also Read: How to Write the Flawless Real Estate Agent Bio
Mammalian Cell Culture:
Mammalian cell values use to produce large, complex proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies. The use of mammalian cells permits modification of the API similar to that which can occur in human cells (e.g., glycosylation). The production processes with mammalian cell cultures take from several days to weeks. The growth of these cells requires a complex and balanced mix of nutrients and relatively mild growth conditions in terms of agitation and aeration.
Microbial Organisms:
Microbial organisms can grow much faster with culture times of several days or even hours. Slighter molecules such as peptides, enzymes, antibody fragments, and protein scaffolds can produce very efficiently. Microbial organisms are usually very robust and can grow to high cell densities, typically several orders of magnitude beyond mammalian cell cultures. Microbial organisms often have some restrictions on protein size and “human-like” modification of molecules.
Downstream Execution
After the protein or antibody molecule generation. The isolation and purification of the complex mixture of proteins from the host cell, cells, cell debris, nutrients, and wastes must now occur.
Purification begins with the separation of cells from the medium. In most mammalian cultures, the protein is secret into the medium, so the supernatant must be collected for further purification. In microbial production, protein can also accumulate in cells; therefore, cells must break down, and cellular debris must separate from the protein of interest. Insoluble products, including attached unfolded pure proteins, called inclusion bodies, must refold to achieve their native and active conformation. Precipitation steps based on temperature, pH, or chemical interaction can use to remove process-related impurities.
Also Read: Midstream Oil Operations Defined
Various techniques purify the solution containing the protein of interest. Chromatographic separation steps widely use; they are based on the principles of separation by charge, size, or hydrophobicity of the protein or by a specific affinity for the chromatographic resin. A wide variety of filtration techniques separate protein from remaining solids, remove impurities, and exchange buffers.
At Boehringer Ingelheim BioXcellence ™, we have extensive experience in a wide variety of host cell and strain types, including cell cultures and microbial organisms (bacteria and yeast) that produce a variety of molecule types. Such as monoclonal, glycosylated, and non-glycosylated antibodies. recombinant. proteins, peptides, antibody fragments, Fc fusion proteins, protein scaffolds, and plasmid DNA. We offer platform solutions for monoclonal antibodies and bespoke solutions based on a large toolbox of manufacturing processes.
Final
Our decades of experience in the development, transfer and scaling of biological processes, combined with modeling tools and a comprehensive characterization of processes, as well as the most modern analysis methods allow us to offer tailor-made solutions for a large number of molecules. , efficient process development and fast and safe supply of material throughout the entire life cycle of a given API.
Related Searches:

